Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 12 (6); November 25, 2022
Volume 12 (6); November 25, 2022
| Assessment of the diets and food security of households hosting and not hosting internally displaced persons in the Kora, Burkina Faso |
Research Paper
Assessment of the diets and food security of households hosting and not hosting internally displaced persons in the Kora, Burkina Faso
Kobyagda B, Hama-Ba F, Tarnagda B, Ouedraogo O, Zoungrana B, Savadogo A.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 12(6): 97-107, 2022; pii:S225199392200012-12
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.12
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.12
Abstract
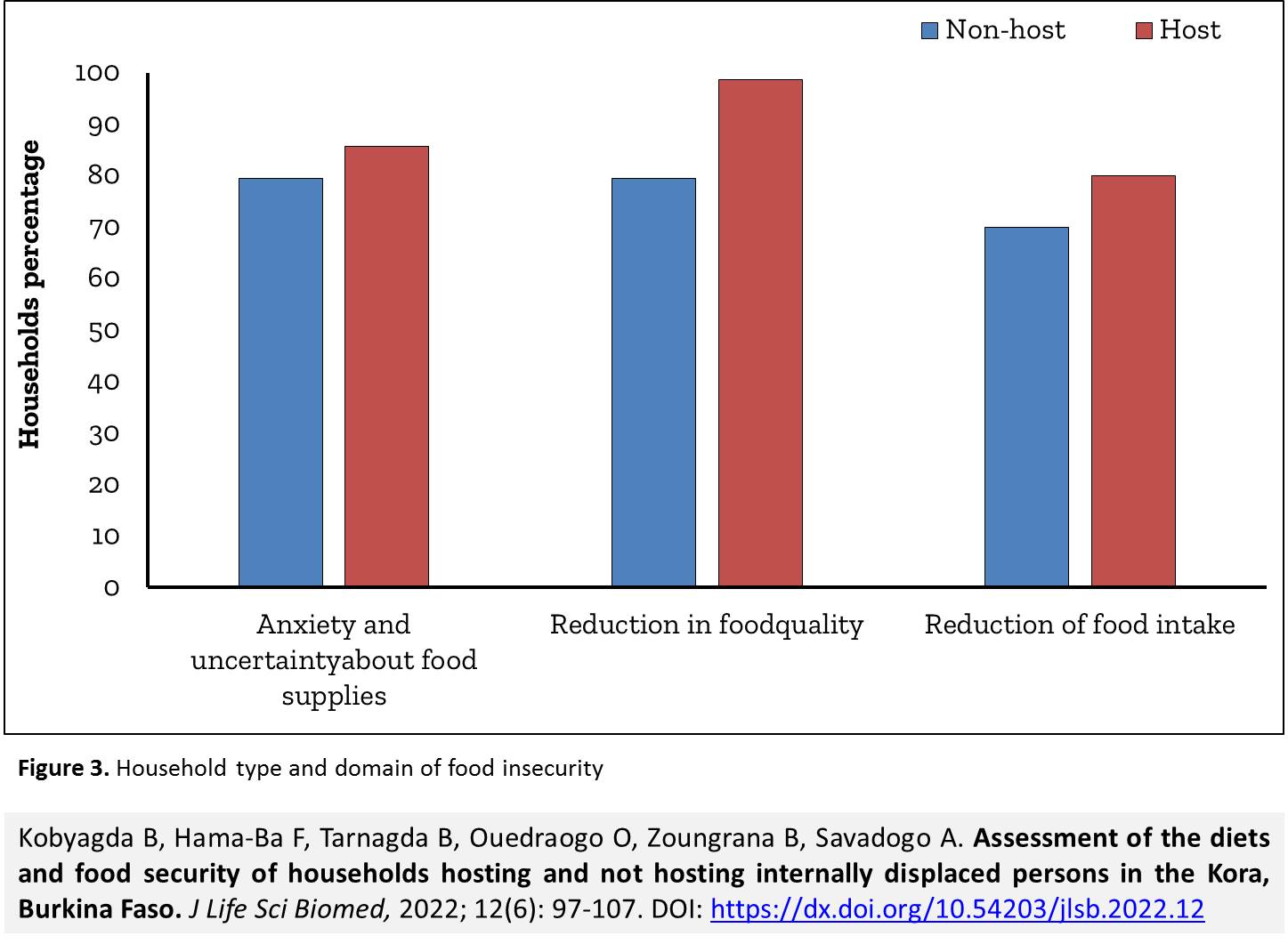
Introduction. Terrorism is escalating in the Sahel region of Africa, forcing massive population displacement and worsening food insecurity. Aim. The objective of the present study was to assess the level of food insecurity within households hosting internally displaced persons (IDP), known as host households, compared to households not hosting internally displaced persons, known as non-host households in the Kora area in Burkina Faso. Methods. A cross-sectional study was conducted in June 2020 at the Kora area and included 70 host households and 73 non-host households. Results. Most of the households had smallholding and were living from subsistence farming. Host households had better quality diets in terms of diet diversification compared to non-host households. In addition, the non-host household were the most vulnerable in terms of food insecurity. Factors associated with household food insecurity were household status (i.e. host or non-host household) and the occupation (i.e. function) of the head of the households. Conclusion. Food assistance received by IDPs improved the quality of food for their host families but did not protect them from food insecurity with all its consequences. Recommendation. The Burkinabe state, in collaboration with the concerned stakeholders should promote good dietary diversity practices, improve food availability and access and monitor host households and provide them with substantial food aid without forget the non-host households which are also exposed.
Keywords: Kora, Food diversity, Food insecurity, Internally displaced persons.
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Survival rates and quality of life of patients after thoracic endovascular aortic repair |
Research Paper
Survival rates and quality of life of patients after thoracic endovascular aortic repair
Zufarov MM, Makhkamov NK, and Khafizov TN.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 12(6): 108-114, 2022; pii:S225199392200013-12
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.13
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.13
Abstract
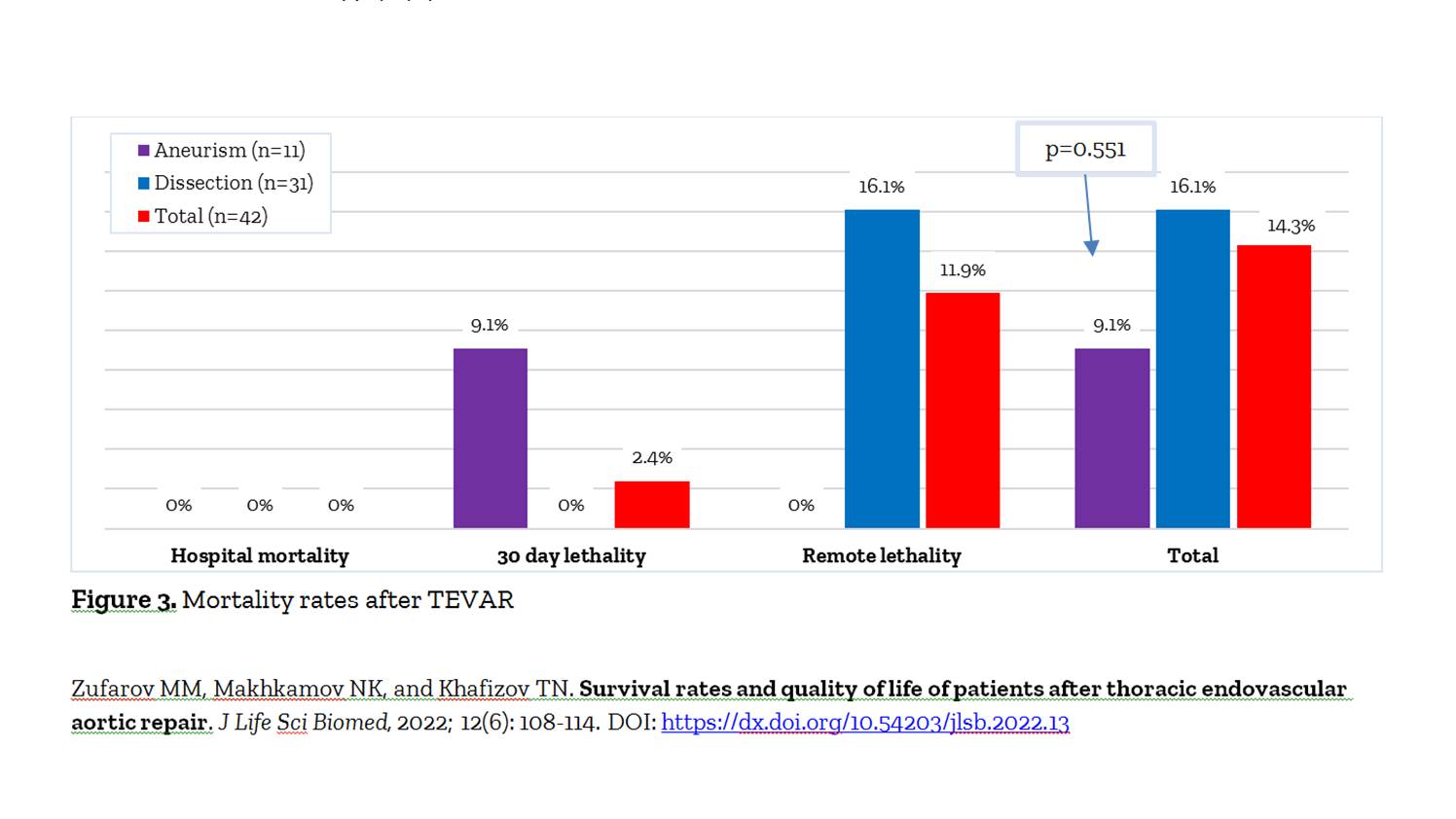
Introduction. Aim. This study aimed to assess patients' quality of life of patients after thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR). Methods. The clinical data of 42 patients (mean age of 58.7±4.1 years, 32 men, 10 women) underwent TEVAR from 2016 to 2022 were analyzed. The mean follow-up period was 2.7±0.25 years. The thoracic aortic aneurysm was diagnosed in 11 out of 42 cases. TEVAR was performed in 31 of 42 patients with aortic dissection (24 cases had type B, 4 cases had type "neither A nor B", and 3 had type A). Hybrid surgeries were performed in 12 patients, including 3 significant surgeries with prosthetics of the ascending and aortic arch, 3 cases with parallel carotid-subclavian bypass, and 6 of patients with stenting of the common carotid artery and endoprosthesis replacement of the left subclavian artery. Results. The cumulative survival rate at 30 days was 97.6%, 6-month survival was 88.1%, and 3-year survival was 85.7%. The dynamics of assessments by SF-36 domains showed that after TEVAR, vital activity and mental health fields were the most effective. So, if before TEVAR in the binding activity domain, the average quality of life was 63.8±7.2, then after 12 months, the indicator increased with a statistically significant differenceto 86.2±6.4 (P<0.001). The patient's mental health improved significantly with SF-36 scores after TEVAR rate of 77.4±4.4. Also. All other domains enhanced considerably compared to the pre-TEVAR survey results (P<0.01). Conclusion. TEVAR showed high efficiency with significant improvement in the general condition and quality of life of patients.
Keywords: Aneurysms and dissections of the thoracic aorta, Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR), Survival, Quality of life
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
| Food consumption and dietary diversity associated with breastfeeding mod of children aged 6-23 months in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso |
Research Paper
Food consumption and dietary diversity associated with breastfeeding mod of children aged 6-23 months in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
Bougma S, Kagambega B, Tapsoba F, Sanou A, Songre-Ouattara LT and Savadogo A.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 12(6): 115-123, 2022; pii:S225199392200014-12
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jlsb.2022.14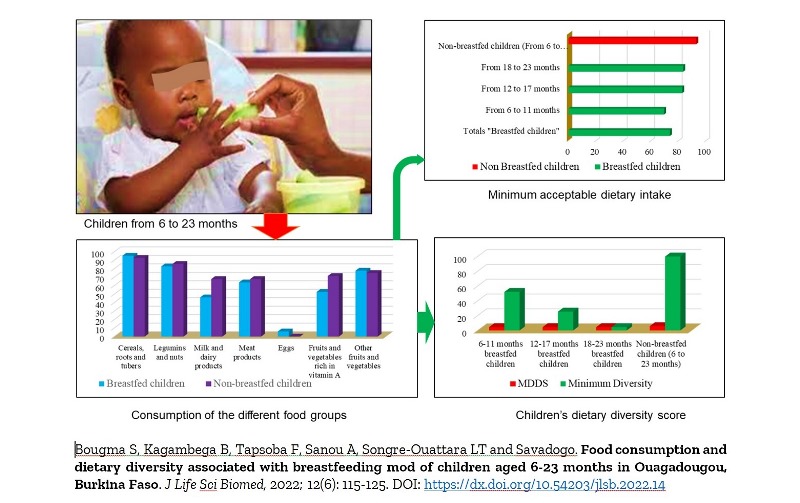 Abstract
Abstract
Background. To provide the essential needs that the body requires, it is necessary to consume a variety of foods. In Burkina Faso, little information is available on the diversity of food consumed by children in major’s urban centers. Aim. The objective of this study was to assess the dietary diversity of children aged from 6 to 23 months and the associated determinants. Methods. The study consisted in the analysis of food data through a cross-sectional survey. Sphinx V5, IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0 and XLSTAT 2016 software were used for data entry and processing. Results. The majority of mothers (50.16%) were between 26 and 35 years old and 95.31% lived with a partner. In total, 41.26% of women had secondary education levels while 44.66% were housewives. Breastfed children largely consumed cereals (95.31%), legumins (83.01%) and fruits (77.67%). Non-breastfed children also consumed mainly cereals (92.86%), legumins (85.71%) and fruits (75%). Minimum dietary diversity was achieved by 100% of non-breastfed children with a Mean Dietary Diversity Score (MDDS) of 5.75 groups versus 81.86% for breastfed children with MDDS of 4.45 food groups. The minimum acceptable diet was reached by 73.73% of breastfed children versus 92.85% for non-breastfed children. The analysis of factors associated with dietary diversity showed a correlation with the mothers’ education levels, the mothers’ occupation, the children’s gender, the number of daily meals and the consumption of some food groups. Conclusion. The food diversity indicators were generally satisfactory.
Keywords: Dietary diversity, Factors associated, Food groups, Minimum acceptable diet, Ouagadougou.
[Full text-PDF] [ePub] [Export citation from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)

