Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 5 (4); July 30, 2015
Research Paper
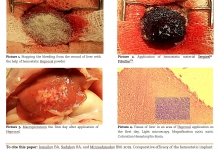
Correlation of the Nerves Number at Three Points Exposed by Laser with Gonadal Maturation of Abalone (Haliotis squamata).
Angga Pebriani D.A., Sri Widodo M. and Rahem Faqih A.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 5(4): 86-90, 2015.; pii:S225199391500018-5
Abstract
Abalone is one of marine commodities which possess high economic value. The demand on abalone in international markets rises every year. Therefore, efforts to improve abalone production are conducted and one of them is by applying laser puncture technology. The purpose of this research is to locate the best point for laser exposure which is based on the nerves distribution in three gonadal parts. Laser exposures were conducted in a home scaled hatchery in Musi Village, Bali. Gonadal tissue preparation was done in Laboratory of Medical Anatomy and Physiology of Medical Faculty, Universitas Brawijaya. The research used descriptive method to see the correlation of the numbers of nerves in three parts of gonads with the speed of abalone gonadal maturation by laser exposures. Variables observed were Gonadal Maturation Stages, Gonado Somatic Index (GSI) and gonadal histology of male and female abalone. The result showed that the best exposure for male abalone was done in posterior part while the mid interior part was best for female abalone.
Key words: Gonad Abalone, Laserpuncture, Oocyte, Nerves, Sperm
[Full text-PDF] [RICeST] [DOAJ]
Research Paper
A study on negative Schemas and resiliency of the quality of life for patients with diabetes.
Noorbakhsh Amiri F, Yaghubi A, Abbasi Asfajir AA.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 5(4): 91-96, 2015.; pii:S225199391500019-5
Abstract
The main goal of present research was to study the negative Schemas and resiliency quality of life for patients with diabetes, which was done by correlation method, Statistical society of this research included 8000 patient with diabetes in Babol city. 215 people were selected as statistical samples randomly by using Cochran` sample size calculation formula. Data was collected by using 4 questionnaires diabetes, short form quality of life (12 questions), Young` schema and resilience criterion of Kater and Davidson. In order to analyze the data, the Pierson correlation, and multiple regression and variance analysis were used. The results of the study showed that primary incompatible schemas have negative and significant relationship with quality of life, but resilience have positive and significant relationship with quality of life. Hence, regarding the results of this research, incompatible schemas and resilience have a determinant role in quality of life for patients with diabetes.
Key words: Diabetes, Negative Schemas, Resilience, Quality of Life.
[Full text-PDF] [RICeST] [DOAJ]
Research Paper
The Effects of Different Intensive Culture Systems on White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Muscle Protein Pattern.
Martini ND, Nursyam H and Fadjar M.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 5(4): 97-101, 2015; pii:S225199391500020-5
Abstract
Application of biofloc system, a heterotrophic culture with minimal water exchange, has gained interest particularly in relation to providing high productivity, low feed-conversion ratios, and a stable culture environment, especially in shrimp. In biofloc system, heterotrophic bacterial tends to form noticeable aggregates (biofloc), which can be consumed by shrimp as a natural protein source. In relation to this, the impact of different culture systems on white shrimp (L. vannamei) muscle protein patterns was investigated. In this research, an SDS-PAGE study was performed on white shrimp muscle tissue along the production cycle in intensive shrimp culture ponds with different culture systems (Phytoplankton, Semi-Biofloc, and Biofloc). The study was located in different areas of the District of Tuban, East Java. The aim of this study was to accomplish systematic characterization of the white shrimp muscle protein pattern, which derives from each of the ponds with different rearing systems. The result of the study showed that the biofloc system yields variability of protein pattern as it maintains good water quality throughout the culture and provides an alternative protein source (as biofloc) for the shrimp besides the pellet.
Key words: White shrimp (L. vannamei), biofloc system, muscle protein pattern, SDS-PAGE
[Full text-PDF] [RICeST] [DOAJ]
Research Paper
Feasibility and Suitability Analysis of Eucheuma cottonii Aquaculture Area in Seriwe Gulf, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.
Pratama FS , Marsoedi, GatutBintoro.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 5(4): 102-105, 2015; pii:S225199391500021-5
Abstract
The purpose of this research is to know the suitability of an area for Eucheuma cottonii seaweed aquaculture in Seriwe gulf of West Nusa Tenggara. Method used in the research is ecological and suitability analysis of the water area (waves, temperature, depth, current velocity, transparency, salinity, dissolved oxygen, pH, total suspended solid, phosphate and nitrate) with a map digitizing using ArcGIS 10.1 software. The results on water quality parameters showed that Station 1 and Station 2 has shown suitable water quality with 0.27-0.3 m of waves, temperature about 28.4-29 0C, 2.6-4.3 m depth, 0.16-0.22 m/s of current velocity, transparency was 2.0-3.3, salinity was 32-35 ppt, dissolved oxygen was 6.63-6.63 ppm, pH 7.4-7.9, total suspended solid was 22.6-14.3, phosphate was 0.64-0.52 ppm and nitrate was 0.57-0.42, while Station 3 showed unsuitable water quality with 0.1 m waves, temperature was 28 0C, depth was 0.8 m, current velocity was 0.07 m/s, transparency was 0.6, salinity was 15.2 ppt, dissolved oxygen was 5.43 ppm, pH 6.78, TSS 24.4, 0.76 ppm phosphate 0.63 ppm nitrate.
Key words: Seaweed, Eucheuma cottonii, Water quality
[Full text-PDF] [RICeST] [DOAJ]
Research Paper
Betanodavirus Infections in Tilapia seed (Oreochromis sp.), in Indonesia
Christi Prihartini N, Yanuhar U and Maftuch
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 5(4): 106-109, 2015.; pii:S225199391500022-5
Abstract
Betanodavirus is the causative agent of the disease VNN (Viral Nerveous Necrosis) and has been reported in many cultured marine fish species worldwide and lately also attacked for freshwater species. In the present study, we described the betanodavirus infection in tilapia seed (Oreochromis sp.). The sample used (5-7 cm in total length) were taken randomly in Central Java, Indonesia. Brain and eyes of fish specimen were divided in two parts, for histopathological examination and for viral isolation using nested RT-PCR. The results showed that tilapia seed infected by VNN, and also showed a clear pathognomic VNN such as vacuolization and inclusion body in the brain and eyes, similar to the pattern of infection in naturally infected marine fish. By phylogenetic analysis, the isolates from tilapia seed belonged to RGNNV genotype (unpublished data). Although still very few reports and there is no outbreak of VNN in tilapia in Indonesia, but this study shows the possibility of that species could be the carrier or reservoir of this virus.
Key words: VNN, tilapia seed (Oreochromis sp.), histopathology, Indonesia
[Full text-PDF] [RICeST] [DOAJ]