Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 7 (3); May 25, 2017 [Booklet]
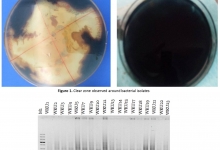
The effects of redundant water quality arameters on chemical composition of Oreochromis niloticus and Bagurs bayad procured from Jebal Aulia Dam and Lake Nubia
Mohammed ME, Sulieman HMA and Ahmed AI.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 7(3): 26-30, 2017; pii:S225199391700005-7
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the effect of some water quality parameter including water temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, chemical oxygen demand and biochemical oxygen demand on chemical composition of Oreochromis niloticus and Bagurs bayad procured from Jebal Aulia Dam and Lake Nubia. The chemical composition of fish muscles was included protein, moisture, fat, and ash contents, using AOAC method. The findings of fat contents were most elevated in Bagurs bayad (10.46+0.47 at Jebal Aulia Dam, and the slightest fat contents were recorded insignificant in Oreochromis niloticus (6.32+0.32) appearing differently in relation to Lake Nubia samples, (P˂ 0.01). Moreover, the protein contents were observed varied slightly in both studied fish at Jebal Aulia and Lake Nubia. Significant contrasts (P˂ 0.01) likewise acknowledged in the Ash contents and were most appeared in O. niloticus in Jebal Aulia. The mean values for moisture content of Oreochromis niloticus were observed a significant difference (P˂ 0.01), at Lake Nubia. Physio-chemical characteristics of the water showed significant variations between the mean values of temperature of Jebal Aulia Dam and Lake Nubia (P˂ 0.05). While there was no significant different in pH levels between both sites. The slight variations of DO, BOD significant deference (P˂ 0.05) and COD appeared on both studied lakes insignificantly (P˂ 0.05).
Keywords: Lake Nubia, Jebel Aulia, Nile fish, proximate analysis.
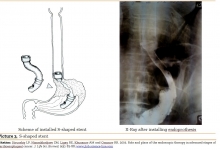
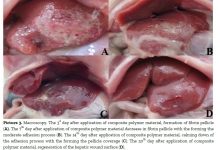
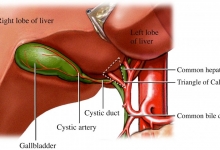
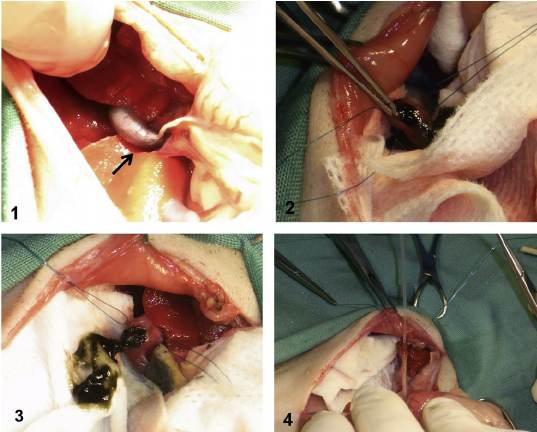
Prospects of Reconstructive and Restorative Surgery of Extrahepatic Biliary Tracts.
Nazirov FG, Akbarov MM, Saatov RR, Turakulov UN.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 7(3): 31-36, 2017; pii:S225199391700006-7
Abstract
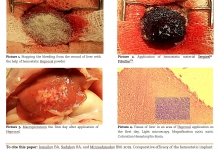
Gallstone disease morbidity, as well as improving biliary tract surgery have led to a significant increase in the amount of surgical interventions in patients with biliary disorders. Since operations on biliary tract today are performed in almost all hospitals by differently-skilled surgeons, this leads to an increased frequency of various complications, including iatrogenic injuries, which are responsible for the formation of cicatricial strictures of extrahepatic bile ducts. The leading hepatology centers continue to accumulate the new clinical data on the treatment of patients with bile duct strictures, continuously and critically reinterpreting views on key issues of this problem. Restoring the adequate bile secretion is a great difficulty. We used classifications proposed by some researchers such as Bismuth, Ratchik and Galperin to review and discuss six key surgical problems of hepatobiliary tract. The main causes of the difficulty are gross violations of topographic and anatomical relationships and commissural processes at the gates of the liver, severe general condition of patients caused by prolonged mechanical jaundice and recurrent purulent cholangitis. A growing interest is arisen by non-invasive methods of restoration by endoscopic interventions. Application of endoscopic methods allows preparing patients for the upcoming scheduled or deferred surgical interventions. In most cases the above endoscopic interventions may be an alternative to surgical interventions. Despite the introduction of high-tech, minimum-invasive diagnostic and treatment methods, the progress in reconstructive surgery of the biliary tract, only long-term results analyses can provide an objective assessment of the correctness of the chosen direction.
Keywords: Bille Duct Injuries, Bille Duct Restorative Surgery, Non-Invasive Methods of Restoration