Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 9 (3); May 10, 2019 [Booklet]![]()
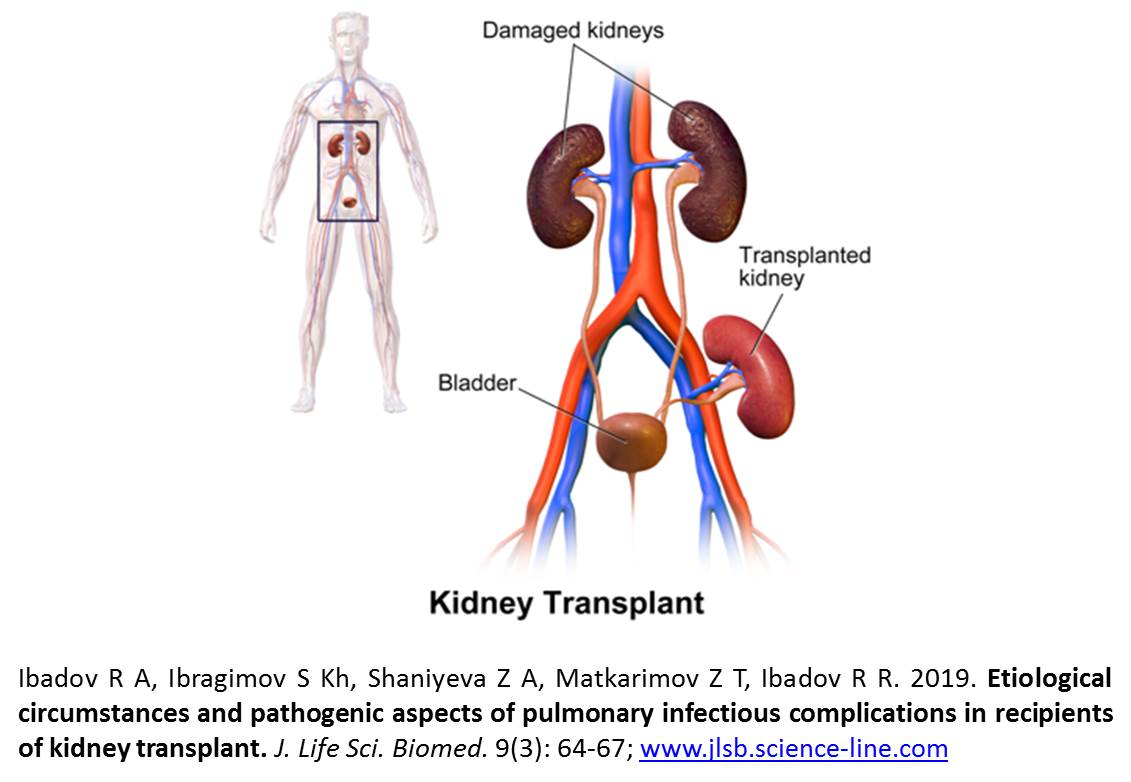
Etiological circumstances and pathogenic aspects of pulmonary infectious complications in recipients of kidney transplant.
Ibadov R A, Ibragimov S Kh, Shaniyeva Z A, Matkarimov Z T, Ibadov R R.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(3): 64-67, 2019; pii:S225199391900010-9
Abstract
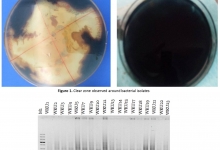
Aim. This study aimed to determine the spectrum of pathogens and its resistance in the dynamics in patients with infectious complications after kidney transplantation. Methods. The results of the study of biomaterials from patients with infectious complications on the background of acute and chronic kidney transplant rejection have been studied. Results. During the analyzed period, there was a tendency to change the spectrum of pathogens, the growth of the value of gram-negative bacteria. The sensitivity analysis of the isolated microorganisms over the study period (2010-2017) showed an increase in the resistance of the dominant pathogens. Also, there was a significant increase in the frequency of occurrence of Candida fungi. Conclusion. In most kidney transplant recipients with nosocomial infections is unavoidable. Therefore, a timely and adequate antibiotic therapy is required to constant control of modern pathogens with increased resistance. Recommendations. The increase in antibiotic resistance of the leading pathogens makes it necessary to study the antibioticogram of all strains isolated from patients for an adequate choice of effective antibiotic therapy. The obtained data should be used to optimize empirical antibiotic therapy in patients with purulent-septic complications after kidney transplantation.
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Immunosuppression, Chronic graft rejection, Infection, Lung damage, Intensive care
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
Review on: biodiversity, ecosystem services and genetically modified organisms.
Birhan M, Dejene H and Kenubih A.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(3): 68-73, 2019; pii:S225199391900011-9
Abstract
Introduction. Understanding the relationship between ecosystem and diversity requires knowledge of how species interact with each other and how each is affected by the environment. It is useful to distinguish between the instantaneous effects of species richness on ecosystems and those which become deceptive on a longer time scale, described here as filter and founder effects. Biological diversity appears to enhance the resilience of desirable ecosystem states, which is required to secure the production of essential ecosystem services. Aim. The diversity of responses to environmental change among species contributing to the same ecosystem function, which we call response diversity, is critical to resilience. Response diversity is particularly important for ecosystem renewal and reorganization following change. Here we criticism the various roles that biodiversity, ecosystem services and genetically modified organisms play in terrestrial ecosystems with special emphasis on their contribution to productivity and diversity. Therefore, the aim of this review is summarizing of different articles and writing of the effects of one to the others, and the relation between biodiversity, ecosystem services and genetically modified organisms.
Keywords: Biodiversity, Ecosystem services, Genetically modified organisms
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]
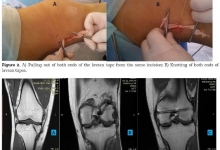
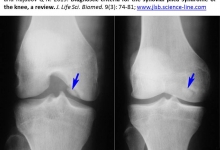
Diagnostic criteria for the synovial plica syndrome of the knee, a review.
Irismetov M E, Tadjinazarov M B, Kholikov A M, Shamshimetov D F, Usmonov F M and Rajabov Q N.
J. Life Sci. Biomed., 9(3): 74-81, 2019; pii:S225199391900012-9
Abstract
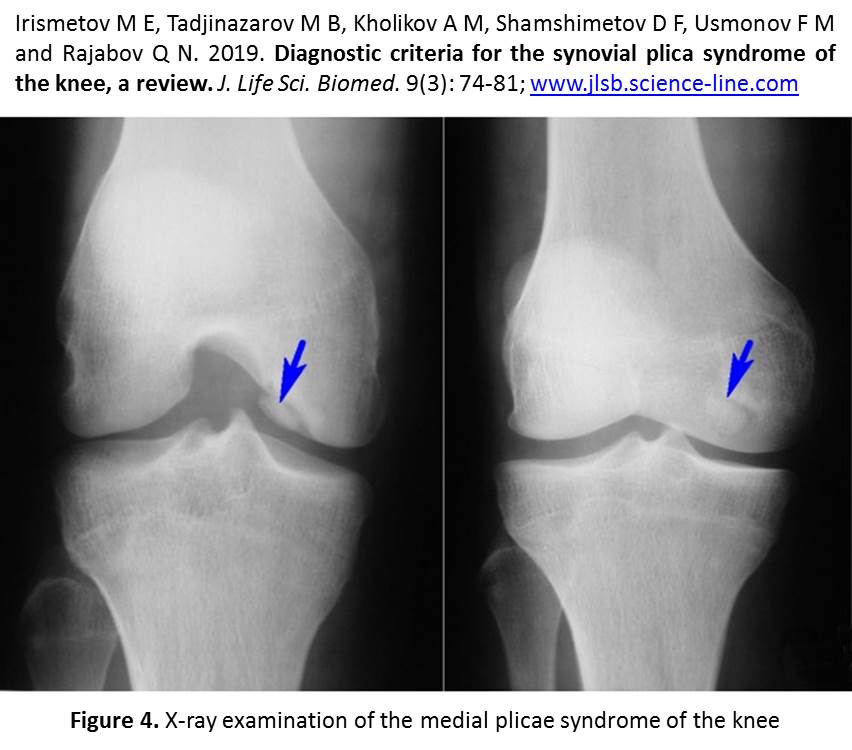
Aim. Based on literature review, the article highlights the current diagnostic criteria for the synovial plicae syndrome (SPS) of the knee. Introduction. The syndrome diagnosis algorithm includes a carefully collected clinical history and clinical examination using specific functional tests, non-invasive research methods (ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging) and arthroscopy. Discussion. It should be noted that the principles of early diagnosis by clinical and radiological methods are still not well understood. Due to non-specific clinical symptoms, this syndrome in most cases is detected by arthroscopic intervention. Conclusion. We try to provide an evidence-based guide to the diagnosis criteria of the knee SPS, based on the analysis of the literature and our own experience.
Keywords: Knee joint, Pain syndrome of the knee, Synovial plicae syndrome, Diagnostic
[Full text-PDF] [HTML] [XML] [Google Scholar]